Black Money and Imposition of Tax Act 2015 MCQs – International Taxation are covered in this Article. Black Money and Imposition of Tax Act 2015 MCQ Test contains 106 questions. Answers to MCQ on Black Money and Imposition of Tax Act 2015 are available after clicking on the answer.
1. What are the key features of the Black Money (undisclosed foreign income and assets) and imposition of Tax Act, 2015?
a) To curb the menace of black money stashed abroad by Indians.
b) To curb the menace of black money stashed in India and abroad by Indians
c) Both A and B
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: c) Both A and B
2. Tax @ …………….. would be paid by every assessee, in respect of his undisclosed foreign income and Undisclosed foreign asset of the previous year
a) 40%
b) 30%
c) 20%
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: c) 20%
3. J is resident and ordinarily resident in India. He has filed income-tax returns with Nil tax till now. His case is picked for scrutiny assessment. AO discovers unexplained investment in house property situated in India. Such such unexplained investment would be taxable @ ……………………..
a) 30% under the provisions of the Black Money Act
b) 60% under Section 115BBE of the Income-Tax Act
c) 30% under Section 115BBE of the Income-Tax Act
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: b) 60% under Section 115BBE of the Income-Tax Act
4. Assessee means a person being a ……………………………..under the Black Money Act
a) Resident and ordinarily resident in India, who has undisclosed foreign income or assets, liable to tax under the Black Money Act
b) Resident but not ordinarily resident in India who has undisclosed foreign income or assets outside India
c) Both A and B
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: a) Resident and ordinarily resident in India, who has undisclosed foreign income or assets, liable to tax under the Black Money Act
5. On which of the following persons, the Black Money Act may be applicable?
a) Individuals/HUFs who are residents and ordinarily resident in India
b) Firm/AOP resident in India
c) Foreign company whose POEM is in India
d) All of the above
Answer
Answer: d) All of the above
6. Which of the following assets may be considered as undisclosed asset located outside India (i.e., foreign assets)?
a) Bank Account outside India
b) Immovable Property outside India
c) Financial interest in an entity located outside India
d) All of the above
Answer
Answer: d) All of the above
7. Choose the asset which would be considered as undisclosed asset located outside India
a) A holds immovable property outside India in his name and he has bought such property from his income declared in his income tax return in India.
b) B holds immovable property outside India as beneficial owner and he has bought such property from his income declared in his income tax return in India.
c) C holds immovable property outside India in his name and he has bought such property from his undisclosed income
d) All of the above
Answer
Answer: c) C holds immovable property outside India in his name and he has bought such property from his undisclosed income
8. Raman has paid Rs 10 crores to purchase a property outside India. However, the property was purchased in the name of his friend Chaman. Who will be considered as beneficial owner of the property outside India?
a) Raman
b) Chaman
c) Both
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: a) Raman
9. In which of the following cases, it is mandatory to file return of income in India?
a) Ram is resident in India and has earned total income of Rs 2,00,000 during the PY 2018-19. However, he has bank account outside India.
b) Shyam is resident in India and has earned total income of Rs 1,50,000 during the PY 2018-19. However, he is the owner of bungalow outside India.
c) Both A and B
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: c) Both A and B
10. Which of the following assets would be considered as undisclosed asset located outside India (i.e., foreign assets)?
a) Sumit is currently a resident of India. However, he was a non-resident in India during PY 2011-12 when he had acquired immovable property outside India out of income which was not chargeable to tax in India.
b) Tom is a non-resident of India. However, he was a resident in India during PY 2011-12 when he had acquired immovable property outside India out of his undisclosed income chargeable to tax in India
c) Both A and B
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: b) Tom is a non-resident of India. However, he was a resident in India during PY 2011-12 when he had acquired immovable property outside India out of his undisclosed income chargeable to tax in India
Black Money and Imposition of Tax Act 2015 MCQs – International Taxation
11. The AO has discovered immovable property outside India in the name of assessee during assessment. In which of the following cases, such property would be considered as undisclosed asset located outside India under the Black Money Act?
a) Assessee has explained to the AO that such property was bought from his income declared in income-tax return in India
b) Assessee is unable to explain the source of investment in such house property outside India
c) Both A and B
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: b) Assessee is unable to explain the source of investment in such house property outside India
12. In which of the following cases, asset acquired by assessee would be considered as undisclosed asset located outside India under the Black Money Act?
a) Ven was employed in a foreign country where he acquired a bungalow out of income earned in that country during the PY 2016-17. Mr. Ven was non-resident for Indian tax purpose during the PY 2016-17.
b) Harry was resident in India during the PY 2016-17 and he has acquired a property outside India during such PY out of income which is exempt from Indian Income-tax Act.
c) Both A and B
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: d) None of the above
13. Select the correct Statement
a) Undisclosed foreign income earned prior to July 1, 2015 are covered under the Black Money Act
b) Undisclosed foreign income earned on or after July 1, 2015 are covered under the Black Money Act
c) Both A and B
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: b) Undisclosed foreign income earned on or after July 1, 2015 are covered under the Black Money Act
14. Which of the following foreign income would be covered under the Black Money Act?
a) Dipen was a tax resident of India during PY 2014-15. He earned rental income from property situated outside India during the PY 2014-15, which was not disclosed in his income-tax return
b) Ritesh was a tax resident of India during PY 2016-17. He earned rental income from property situated outside India during the PY 2016-17, which was not disclosed in his income-tax return
c) Both A and B
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: b) Ritesh was a tax resident of India during PY 2016-17. He earned rental income from property situated outside India during the PY 2016-17, which was not disclosed in his income-tax return
15. Undisclosed asset located outside India shall be charged to tax on its value [i .e ., fair market value as per Rule 3(1)] in the previous year in which ………………………………
a) The asset was purchased
b) The asset was sold
c) The asset comes to the notice of the Assessing Officer
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: c) The asset comes to the notice of the Assessing Officer
16. Ankush has purchased asset outside India during PY 2001-02 from his undisclosed income earned in India. Such asset was discovered by AO during PY 2016-17. In which year, such undisclosed asset would be charged to tax under the Black Money Act?
a) 2016-17
b) 2001-02
c) Either A or B, at the option of assessee
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: a) 2016-17
17. Sumita acquired a bungalow in UK in January, 1980 when she was resident in India, out of undisclosed income chargeable to tax in India. The AO discovered such bungalow in the PY 2017-18. Market value of bungalow of PY……………….would be charged to tax under the Black Money Act.
a) 1979-1980
b) 2017-18
c) A or B, whichever is high
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: b) 2017-18
18. Anil has opened a bank account outside India during the PY 2011-12. The AO has discovered such bank account during the PY 2017-18. Bank balance on various dates are given as under:
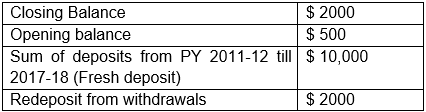
Which of the following value would be considered for valuation under the Black Money Act?
a) $ 2,000
b) $ 10,000
c) $ 500
d) $ 1250
Answer
Answer: b) $ 10,000
19. What would be the fair market value of bullion / Jewellery / precious stone under the Black Money Act?
a) Cost of acquisition
b) Price it would ordinarily fetch in the open market on valuation date
c) A or B, whichever is high
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: c) A or B, whichever is high
20. What would be the fair market value of archaeological collections, drawings, paintings, sculptures or work of art under the Black Money Act?
a) Cost of acquisition
b) Price it would ordinarily fetch in the open market on the valuation date
c) A or B, whichever is high
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: c) A or B, whichever is high
Black Money and Imposition of Tax Act 2015 MCQs – International Taxation
21. In which of the following cases, report from valuer is required under the Black Money Act?
a) For valuation of Bullion / jewellery / precious stones
b) For valuation of archaeological collections, drawings, paintings, sculptures or work of art
c) Both A and B
d) Quoted shares, actively traded in the market.
Answer
Answer: c) Both A and B
22. What would be the fair market value of quoted shares under the Black Money Act when there is trading in such shares in the securities market?
a) Cost of Acquisition
b) Highest price of such shares in the securities market
c) Average of lowest and highest price of such shares in the securities market
d) A or B, whichever is high
Answer
Answer: d) A or B, whichever is high
23. What would be the fair market value of quoted shares under the Black Money Act when there is trading in such shares in the securities market?
a) Cost of Acquisition or Average of lowest and highest price of such shares in the securities market on a date immediately preceding the valuation date, whichever is high
b) Cost of Acquisition or Average of lowest and highest price of such shares in the securities market on valuation date, whichever is higher
c) Cost of Acquisition or Average of lowest and highest price of such shares in the securities market on valuation date, whichever is lower
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: b) Cost of Acquisition or Average of lowest and highest price of such shares in the securities market on valuation date, whichever is higher
24. What would be the fair market value of quoted shares under the Black Money Act when there is no trading in such shares in the securities market?
a) Cost of Acquisition
b) Average of lowest and highest price of such shares in the securities market on a date immediately preceding the valuation date, when there is trading in such shares.
c) A or B whichever is higher
d) A or B whichever is lower
Answer
Answer: c) A or B whichever is higher
25. What would be the fair market value of Unquoted shares (other than equity shares) under the Black Money Act?
a) Cost of acquisition
b) Price it would ordinarily fetch in the open market on the valuation date
c) A or B, whichever is higher
d) A or B, whichever is lower
Answer
Answer: c) A or B, whichever is higher
26. What would be the valuation of an asset (other than bank account) under the Black Money Act, where such asset was transferred for adequate consideration before the valuation date?
a) Cost of acquisition
b) Sale Price
c) Fair Market Value on the date of transfer
d) A or B, whichever is higher
Answer
Answer: d) A or B, whichever is higher
27. What would be the valuation of an asset (other than bank account) under the Black Money Act, where such asset was transferred for inadequate consideration before the valuation date?
a) Cost of acquisition
b) Fair market value on valuation date
c) Fair Market Value on the date of transfer
d) A or C, whichever is high
Answer
Answer: d) A or C, whichever is high
28. A house property (H1) located outside India was bought in 1997 for Rs 20 lakh. It was sold in 2001 for Rs 25 lakh rupees which were deposited in a foreign bank account (BA). In 2002 another house property (H2) was bought for Rs 30 lakh. The investment in H2 was made through withdrawal from BA. Determine the fair market value (FMV) of H1 assuming value of BA and H2 are additionally calculated for Black Money Act and taxed as such.
a) Nil
b) Rs 25 Lakhs
c) Rs 20 lakhs
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: a) Nil
29. Where fair market value of an asset under the Black Money Act is determined in one of the RBI permitted currencies under FEMA, such fair market value shall be converted into Indian currency as per the RBI reference rate of such currency on the ………
a) Date of transfer
b) Valuation date
c) March 31 of the relevant PY.
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: b) Valuation date
30. Where fair market value of an asset under the Black Money Act is determined in a non RBI permitted currency then such fair market value shall be converted into US Dollar on the …………………….as per the rate specified by the Central Bank of the country or jurisdiction in which the asset is located and which would be converted into Indian currency as per the RBI reference rate on the …………………..
a) Date of transfer
b) Valuation date
c) March 31 of the relevant PY.
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: b) Valuation date
Black Money and Imposition of Tax Act 2015 MCQs – International Taxation
31. Which of the following income would be taxable under the Black Money Act?
a) Where ITR is filed but the Foreign income has not been disclosed in the ITR
b) Where there is foreign income but no ITR is filed
c) Both A and B
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: c) Both A and B
32. Indian resident has earned rental income from a property situated outside India during the PY 2016-17, which was not disclosed in his ITR. Such rental income would be taxable as……………………………
a) Undisclosed foreign income under the Black Money Act
b) Undisclosed income under the Income-Tax Act
c) Either A or B, whichever is more beneficial from tax collection perspective
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: a) Undisclosed foreign income under the Black Money Act
33. Select the correct statement
a) Provisions of the Black Money Act for undisclosed foreign income, is a part of the Income-Tax Act
b) The income included in the total undisclosed foreign income and asset under the Black Money Act, shall form part of the total income under the Income-tax Act
c) Provisions of the Black Money Act for undisclosed foreign income is a part of separate chapter other than Income-Tax Act.
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: c) Provisions of the Black Money Act for undisclosed foreign income is a part of separate chapter other than Income-Tax Act.
34. While computing the undisclosed foreign income under the Black Money Act, which of the following relief would be available?
a) Deduction of expenditure incurred to earn such foreign income
b) Set-off of losses of any other business with the undisclosed foreign income
c) Both
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: d) None of the above
35. While computing the undisclosed Black Money, there shall be allowed a deduction from the value of undisclosed foreign asset of ….…………………………………when such asset was acquired out such income
a) Undisclosed foreign income earned before July 1, 2015 and it has been assessed to tax under the Income-Tax Act
b) Income which is assessable under the Black Money Act (i.e., any foreign income which is assessable under the Black Money Act);
c) Both A and B
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: c) Both A and B
36. Where assessee does not have any income assessable under the Income-Tax Act, tax authority having jurisdiction in his case under the Black Money Act would be the one which has jurisdiction in respect of the area in which assessee……….. : –
a) Resides
b) Carries on its business
c) Has its principal place of business
d) All of the above
Answer
Answer: d) All of the above
37. Any tax authority below the rank of Commissioner may impound books of account / documents under the Black Money Act and retain in his custody any such books or documents for a period of …………….. without obtaining the approval of the Principal Chief Commissioner or the Chief Commissioner or the Principal Commissioner or the Commissioner
a) 60 days
b) 30 days
c) 15 days
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: b) 30 days
38. The time limit for passing an order of assessment or reassessment u/s 10 of the Black Money Act is ………….in which notice u/s 10(1) is issued by the Assessing Officer. [Section 11(1)]
a) 2 years from the end of month
b) 3 years from the end of the Financial Year
c) 2 years from the end of the financial year
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: c) 2 years from the end of the financial year
39. An order of fresh assessment in pursuance of order passed u/s 18 of the Black Money Act [setting aside an assessment] may be made at any time before expiry of ………………………………………………….
a) 2 years from the end of the FY in which order u/s 18 is issued
b) 2 years from the end of the FY in which order u/s 18 is received by Principal Commissioner or Commissioner
c) 3 years from the end of the FY in which order u/s 18 is received by Principal Commissioner or Commissioner
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: b) 2 years from the end of the FY in which order u/s 18 is received by Principal Commissioner or Commissioner
40. Select the correct statement
a) The time-limit of 2 years u/s 11(1) for assessment or reassessment under the Black Money Act shall apply even when such assessment or reassessment is made in the consequence of, or to give effect to, any finding or direction contained in the order of any Appellate authority or a court
b) The period during which the assessment proceeding is stayed by an order or injunction of any court shall be excluded while computing limitation period of 2 years for completing assessment under the Black Money Act
c) Both A and B
d) Time limit taken in passing the order by the AO.
Answer
Answer: b) The period during which the assessment proceeding is stayed by an order or injunction of any court shall be excluded while computing limitation period of 2 years for completing assessment under the Black Money Act
Black Money and Imposition of Tax Act 2015 MCQs – International Taxation
41. Which of the following time-period shall be excluded in computing limitation period of assessment under the Black Money Act?
a) The period commencing from the date on which a reference for exchange of tax information is made with foreign tax authority and ending with the date on which the information requested is last received or a period of one year, whichever is less
b) Time taken by assessing authority to pass the assessment order
c) Both A and B
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: a) The period commencing from the date on which a reference for exchange of tax information is made with foreign tax authority and ending with the date on which the information requested is last received or a period of one year, whichever is less
42. If after exclusion of time taken to receive tax information from foreign tax authority and the period during which assessment proceeding is stayed is less than ………..then period of limitation under the Black Money Act shall be deemed to be extended to ……. ?
a) 60 days
b) 90 days
c) 30 days
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: a) 60 days
43. Rectification shall be made within a period of …………………………………………….in which the order sought to be amended was passed under the Black Money Act?
a) 2 years from the end of the Financial year
b) 4 years from the end of the financial year
c) 4 years from the end of the month
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: b) 4 years from the end of the financial year
44. The tax authority may make an amendment in its order under the Black Money Act…………………..: –
a) On its own motion
b) On an application made by assessee
c) On an application made by Assessing Officer
d) All of the above
Answer
Answer: d) All of the above
45. Where a tax authority receives an application from the assessee or the Assessing Officer for amendment of an order under the Black Money Act, such application shall be decided within a period of …………………………….in which the application is received by it
a) 3 months from the end of the month
b) 6 months from the end of the month
c) 6 months from the end of the FY
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: b) 6 months from the end of the month
46. Which of the following persons can file appeal before Commissioner (Appeals) under the Black Money Act?
a) Any person who objects to tax amount on undisclosed foreign income and asset assessed by the AO
b) Any person who denies his liability to be assessed under the Black Money Act
c) Any person who objects to any penalty imposed by the AO under the Black Money Act
d) All of the above
Answer
Answer: d) All of the above
47. Appeal filed before the Commissioner (Appeals) under the Black Money Act shall be accompanied by filing fee of ……….
a) Rs 1,000
b) 10,000
c) Rs 20,000
d) Rs 5,000
Answer
Answer: b) 10,000
48. Where notice of demand is served to an assessee under the Black Money Act, an appeal may be filed before the Commissioner (Appeals) within a period of ……………………..
a) 30 days from the date of service of demand notice
b) 30 days from the date of issue of demand notice
c) 60 days from the date of service of demand notice
d) 60 days from the date of issue of demand notice
Answer
Answer: b) 30 days from the date of issue of demand notice
49. Where no notice of demand is served to an assessee under the Black Money Act, an appeal may be filed before the Commissioner (Appeals) within a period of ……………………..
a) 30 days from the date of which the intimation of order sought to be appealed against is served
b) 60 days from the date of which the intimation of order sought to be appealed against is served
c) 30 days from the date of which the intimation of order sought to be appealed against is issued
d) 60 days from the date of which the intimation of order sought to be appealed against is issued
Answer
Answer: a) 30 days from the date of which the intimation of order sought to be appealed against is served
50. The Commissioner (Appeals) may admit an appeal after expiry of 30 days under the Black Money Act if he is satisfied that appellant has sufficient cause for not filing appeal within that period. However, he can condone delay in filing appeal upto ……………………..
a) 2 years
b) 3 years
c) 1 year
d) 4 years
Answer
Answer: c) 1 year
Black Money and Imposition of Tax Act 2015 MCQs – International Taxation
51. Who can file appeal before Appellate Tribunal under the Black Money Act?
a) Any assessee who is aggrieved by an order passed by the Commissioner (Appeals) or Principal Commissioner or Commissioner
b) AO on a direction received from the Principal Commissioner or Commissioner
c) Both A and B
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: c) Both A and B
52. Under the Black Money Act, an appeal shall be filed by Assessee before the Appellate Tribunal within a period of ………………………………………..-
a) 60 days from the date on which the order sought to be appealed against is issued to the assessee
b) 60 days from the date on which the order sought to be appealed against is communicated to the assessee
c) 30 days from the date on which the order sought to be appealed against is communicated to the assessee
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: b) 60 days from the date on which the order sought to be appealed against is communicated to the assessee
53. An appeal may be admitted by Appellate Tribunal under the Black Money Act after expiry of 60 days on which order is passed. However, such delay may be condoned only when Appellate Tribunal if the delay in filing appeal does not exceed…………………
a) 2 years
b) 1 year
c) 3 year
d) 6 months
Answer
Answer: b) 1 year
54. Assessing Officer or the assessee may file a memorandum of cross objections on receipt of notice that an appeal against the order of Commissioner (Appeals) has been preferred by the other party under the Black Money Act, within a period of ………………….from the date of receipt of such notice
a) 60 days
b) 30 days
c) 15 days
d) 90 days
Answer
Answer: b) 30 days
55. Memorandum of cross objections may be admitted by Appellate Tribunal under the Black Money Act after expiry of 30 days if it is satisfied that there was sufficient cause for not filing appeal within that period and delay in filing memorandum of cross objection does not exceed…………………
a) 1-year
b) 2-year
c) 3-year
d) 6 months
Answer
Answer: a) 1-year
56. Where the appeal is made by the assessee company before the Appellate Tribunal under the Black Money Act, the form of appeal, the grounds of appeal; and the form of verification appended thereto shall be signed by …………………
a) The assessee company
b) The person who is authorised to sign the return of income u/s 140 of the Income-tax Act.
c) Both A and B
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: b) The person who is authorised to sign the return of income u/s 140 of the Income-tax Act.
57. Every appeal filed by the assessee to the Appellate Tribunal under the Black Money Act shall be accompanied by fee of ……………….
a) Rs 10,000
b) Rs 1,000
c) Rs 50,000
d) 25,000
Answer
Answer: d) 25,000
58. When can an appeal be filed before the High Court under the Black Money Act?
a) An appeal can be filed to the High Court against every order passed by Tribunal
b) An appeal can be filed to the High Court against every order passed by Tribunal, if High Court is satisfied that the case involves a substantial question of law
c) An appeal can be filed to the High Court against every order passed by Tribunal, which involves question of law
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: b) An appeal can be filed to the High Court against every order passed by Tribunal, if High Court is satisfied that the case involves a substantial question of law
59. Under the Black Money Act, the appeal shall be filed before the High Court within ………………..from the date on which the order appealed against is received by the Principal Chief Commissioner / Chief Commissioner / Principal Commissioner / Commissioner / Assessee
a) 60 days
b) 30 days
c) 90 days
d) 120 days
Answer
Answer: d) 120 days
60. When can an appeal be made before the Supreme Court against Judgment of High Court, delivered under the provisions of Black Money Act?
a) Appeal can be made before the Supreme Court against every order of the High Court
b) Order of High Court can be challenged before the Supreme Court, when the High Court certifies it to be a fit case for appeal to the Supreme Court.
c) Appeal can be made before the Supreme Court against every order of High Court which involves question of law
d) None of the above
Black Money and Imposition of Tax Act 2015 MCQs – International Taxation
Answer
Answer: b) Order of High Court can be challenged before the Supreme Court, when the High Court certifies it to be a fit case for appeal to the Supreme Court.
61. The revision order passed by the Principal Commissioner or Commissioner u/s 23 of the Black Money Act which is prejudicial to revenue may………………………………………..
a) Enhance the assessment
b) Modify the assessment
c) Cancel the assessment and direct fresh assessment
d) Both A and B
Answer
Answer: d) Both A and B
62. Revision order shall not be passed by the Principal Commissioner or Commissioner, which is prejudicial to the interest of revenue under provisions of the Black Money Act after expiry of ………………………………..in which the order sought to be revised was passed
a) 4 years from end of the financial year
b) 2 years from end of the month
c) 2 years from end of the financial year
d) 4 years from end of the month
Answer
Answer: c) 2 years from end of the financial year
63. Which of the following period shall not be included in computing the limitation period for passing revision order by Principal Commissioner or Commissioner, which is prejudicial to revenue under the provisions of the Black Money Act?
a) Time taken in giving opportunity of being heard
b) Time taken in giving opportunity of being heard in case of change in tax authority
c) The period during which any proceeding is stayed by an order or injunction of any court
d) Both B and C
Answer
Answer: d) Both B and C
64. When an order passed by tax authority shall be deemed to be erroneous in so far as it is prejudicial to interest of revenue under the provisions of the Black Money Act?
a) When an order is passed without giving opportunity of being heard to the assessee
b) When order has not been made in accordance with any order, direction or instruction issued by the Board
c) When an order is passed without the considering the judgment which is favourable to the assessee
d) All of the above
Answer
Answer: b) When order has not been made in accordance with any order, direction or instruction issued by the Board
65. Which of the following orders cannot be revised by the Principal Commissioner or Commissioner (other than the order which is prejudicial to the interest of the revenue) under the provisions of the Black Money Act?
a) Order for which time for filing an appeal before the Commissioner (Appeals) has not expired
b) Order against which an appeal is pending before the Commissioner (Appeals)
c) Both A and B
d) Order considered but not decided in an appeal
Answer
Answer: b) Order against which an appeal is pending before the Commissioner (Appeals)
66. The assessee shall make the application for revision of any order, within a period of………………………………..under the provisions of the Black Money Act
a) 1 year from the date on which the order sought to be revised was communicated to him
b) 1 year from the date on which he otherwise came to know of the order sought to be revised
c) 2 year from the date on which the order sought to be revised was communicated to him
d) A or B, whichever is earlier
Answer
Answer: d) A or B, whichever is earlier
67. The Principal Commissioner or the Commissioner may admit the application after the expiry of one year, if he is satisfied that the Assessee was prevented by sufficient cause from making an application. However, the application shall be made before expiry of………………………………………….
a) 1 year from the date on which the order sought to be revised was communicated to him
b) 2 year from the date on which the order sought to be revised was communicated to him
c) 2 year from the date on which he otherwise came to know of the order sought to be revised
d) B or C, whichever is earlier
Answer
Answer: d) B or C, whichever is earlier
68. Where application for revision is made by the assessee no revision order shall be passed after expiry of …………………….. under the provisions of the Black Money Act
a) 1 year from end of the month in which application is made by assessee
b) 2 year from end of the FY in which application is made by assessee
c) 1 year from end of the FY in which application is made by assessee
d) 2 year from end of the FY in which application is made by assessee
Answer
Answer: c) 1 year from end of the FY in which application is made by assessee
69. Where order is revised by Commissioner suo-motu, no revision order shall be passed after expiry of …………………….. under the provisions of the Black Money Act
a) 1 year from the date of order sought to be revised
b) 2 year from the date of order sought to be revised
c) 1 year from the end of the month in which order sought to be revised was passed
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: a) 1 year from the date of order sought to be revised
70. Any amount payable in notice of demand under the Black Money Act shall be paid within a period of …………….from the service of notice of demand
a) 15 days
b) 60 days
c) 30 days
d) 90 days
Answer
Answer: c) 30 days
Black Money and Imposition of Tax Act 2015 MCQs – International Taxation
71. Select the correct statement
a) The period of 30 days for payment of demand under the Black Money Act may not be reduced by AO
b) The period of 30 days for payment of demand under the Black Money Act may be reduced by AO if he has reason to believe that allowing such time would be detrimental to the interests of revenue, but with the previous approval of the Joint Commissioner
c) Both A and B
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: b) The period of 30 days for payment of demand under the Black Money Act may be reduced by AO if he has reason to believe that allowing such time would be detrimental to the interests of revenue, but with the previous approval of the Joint Commissioner
72. The Assessing Officer may extend the time for payment of demand or allow payment by installment under the provisions of the Black Money Act if an application is made by assessee before the expiry of ………………….
a) 60 days period for payment of demand
b) 30 days period for payment of demand
c) Reduced period for payment of demand
d) B or C, whichever is applicable
Answer
Answer: d) B or C, whichever is applicable
73. Who would be the tax recovery officer under the provisions of the Black Money Act?
a) The officer, within whose jurisdiction the assessee carries on business
b) The officer, within whose jurisdiction the principal place of business of the assessee is situated
c) Either A or B
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: c) Either A or B
74. When there is a process to liquidate the assessee-company liable to pay tax under the provisions of the Black Money Act, there would be appointment of liquidator. Such liquidator has to inform his appointment to the Assessing Officer having jurisdiction to assess the undisclosed foreign income and asset of the company within a period of …………………..of his appointment
a) 60 days
b) 90 days
c) 30 days
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: c) 30 days
75. Where the amount of tax under the Black Money Act cannot be recovered from the company, then every person being a …………………………………would bejointly and severally liable for the payment of any amount due under the Black Money Act.
a) Manager during the whole Financial Year in which tax default has been made
b) Manager at any time during the financial year in which tax default has been made
c) Manager at any time upto the end of financial year in which tax default has been made
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: b) Manager at any time during the financial year in which tax default has been made
76. Which of the following interest liability would arise when assessee did not file the income-tax return to disclose foreign income?
a) Section 234A
b) Section 234B
c) Section 23C
d) All of the above
Answer
Answer: d) All of the above
77. How much maximum penalty may be levied where there is undisclosed foreign income of Rs 10 lakhs – Assume tax rate of 30 % ?
a) Rs 3 lakhs
b) Rs 6 lakhs
c) Rs 9 lakhs
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: c) Rs 9 lakhs
78. Failure to file return of income by resident assessee would invite penalty of ……………….. if such person held any asset located outside India.
a) Rs 5 lakhs
b) Rs 1 lakh
c) Rs 10 lakhs
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: c) Rs 10 lakhs
79. Any person, being a resident and ordinarily resident in India would be liable to penalty of ……………… if such person fails to furnish any information or furnishes inaccurate particulars in return of income relating to any asset located outside India
a) Rs 5 lakhs
b) Rs 1 lakh
c) Rs 10 lakhs
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: c) Rs 10 lakhs
80. In which of the following cases, penalty shall not be levied even if person resident in India fails to furnish any information in return of income relating to any bank account outside India?
a) When assessee offers genuine explanation for such failure
b) When the amount of tax is less than Rs 5 lakhs
c) When such bank accounts outside India have an aggregate balance of Rs 5 lakhs or less at any time during the PY
d) All of the above
Answer
Answer: c) When such bank accounts outside India have an aggregate balance of Rs 5 lakhs or less at any time during the PY
Black Money and Imposition of Tax Act 2015 MCQs – International Taxation
81. For determining the value in INR of the balance in an foreign bank account, the rate of exchange shall be the …………………………of such foreign currency as on the date for which the value is to be determined, as adopted by the State Bank of India constituted under the SBI Act, 1955
a) Telegraphic Transfer selling rate
b) Telegraphic Transfer buying rate
c) Average of Telegraphic Transfer Buying rate and selling rate
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: b) Telegraphic Transfer buying rate
82. What would be the penalty for default in payment of tax arrear under the provisions of the Black Money Act?
a) 100% of tax in arrear
b) 200% of tax in arrear
c) 300% of tax in arrear
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: a) 100% of tax in arrear
83. In which of the following cases penalty shall not be levied for continuing default in payment of tax arrears under the provisions of the Black Money Act?
a) When tax has been paid before levy of such penalty
b) When tax has been paid after levy of such penalty
c) When assessee has genuine reason for non-payment of tax arrear
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: d) None of the above
84. What is the time-limit for issuing show-cause notice before levying penalty @ 300% of tax on undisclosed foreign income?
a) During pendency of proceedings under the Black money Act.
b) Within a period of 5 years from the end of FY in which default was committed
c) Within a period of 2 years from the end of FY in which default was committed
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: a) During pendency of proceedings under the Black money Act.
85. An order imposing a penalty under the Black Money Act shall be made with the approval of the…………………., if the amount of penalty is more than Rs. 1 lakh and the tax authority levying the penalty is in the rank of Income-tax Officer
a) Deputy Commissioner
b) Assistant Commissioner
c) Joint Commissioner
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: c) Joint Commissioner
86. A penalty order under the Black Money Act cannot be passed after expiry of………………………………………., in which the notice for imposition of penalty is issued under section 46 (i.e., show cause notice under Section 46)
a) 2 year from the end of the financial year
b) 1 year from the end of the month
c) 1 year from the end of the financial year
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: c) 1 year from the end of the financial year
87. An order revising the penalty under the Black Money Act cannot be passed after the expiry of ………………………………………..in which order of the Commissioner (Appeals), the Appellate Tribunal, the High Court or the Supreme Court is received by the Principal Chief Commissioner or the Chief Commissioner or the Principal Commissioner or the Commissioner :-
a) One year from the end of the month
b) One month from the end of the month
c) six months from the end of the year
d) six months from the end of the month
Answer
Answer: d) six months from the end of the month
88. Which of the following shall be excluded for computing the period of limitation for imposition of penalty under the Black Money Act?
a) Time taken in giving an opportunity of being heard to the assessee in case of change in tax authority
b) The period during which a proceeding for the levy of penalty is stayed by an order, or injunction, of any Court
c) Time taken by authority for passing penalty order
d) Both A and B
Answer
Answer: d) Both A and B
89. Any person, being a resident and ordinarily resident in India would be punishable with rigorous imprisonment of ……………………………………. when there is any willful failure to furnish return u/s 139(1) of the Income tax Act in due time, and such person held any asset located outside India
a) 2 years
b) 1 year to 7 years
c) 6 months to 7 years
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: c) 6 months to 7 years
90. Any person, being a resident and ordinarily resident in India would be punishable with rigorous imprisonment of ……………………………………. when there is any willful failure to furnish information of foreign income in return of income u/s 139(1) of the Income tax Act in due time
a) 2 years
b) 6 years to 7 years
c) 6 months to 7 years
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: c) 6 months to 7 years
Black Money and Imposition of Tax Act 2015 MCQs – International Taxation
91. There will not be any prosecution for failure to furnish return of income when assessee holds any foreign asset and such return of income is furnished before …………………………
a) Expiry of the one year from the end of assessment year
b) Expiry of the assessment year
c) Expiry of the two year from the end of the Assessment Year
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: b) Expiry of the assessment year
92. Where any person being a resident and ordinarily resident in India willfully attempts to evade any tax, penalty or interest under the Black Money Act, he shall be punishable with rigorous imprisonment of …………………
a) 6 months to 7 years with fine
b) One year
c) 3 years to 10 years with fine
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: c) 3 years to 10 years with fine
93. Which of the following would be considered as willful attempt to evade tax, penalty, etc. under the Black Money Act?
a) Where any person has in his possession or control any books of account or other documents containing a false entry or statement
b) Where any person makes or causes to be made any false entry or statement in books of account or other documents
c) Where any person has failed to file return of income within the due date under Section 139
d) Both A and B
Answer
Answer: d) Both A and B
94. A person shall be punishable with rigorous imprisonment of ………………. if such person makes a statement in any verification under the Black Money Act, or delivers an account or statement, which is false, and which he either knows or believes to be false
a) One year
b) Six months to seven years
c) Six months to one year
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: b) Six months to seven years
95. A person shall be punishable with rigorous imprisonment of ……………….if such person Abets or induces another person to make and deliver an account relating to tax payable which is false and which he knows to be false
a) One year
b) Six months to seven years
c) Six months to one year
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: b) Six months to seven years
96. Where an offence under the Black Money Act has been committed by a company,……………………………………………………………………………………..would be deemed to be guilty of the offence, and would be liable to be proceeded against and punished accordingly
a) Every person who was in charge of company at any time during the year in which offence was committed
b) Every person who was in charge of company at the time when offence was committed
c) The company in which the offence was committed
d) Both B and C
Answer
Answer: d) Both B and C
97. Where an offence under the Black Money Act has been committed by a company, then every person being in charge of the company would be deemed to be guilty of the offence. However, such person would not be deemed to be guilty of offence when ………………………………
a) Such person proves that offence was committed without his knowledge
b) Such person proves that he had exercised all due diligence to prevent such offence
c) Such person has paid due taxes on basis of notice of demand issued by tax authority
d) Both A and B
Answer
Answer: d) Both A and B
98. Any person being…………………….shall be deemed to be guilty of offence under the Black Money Act and shall be liable to be proceeded against and punished accordingly, where an offence has been committed by a company, and
it is proved that the offence has been committed with the consent or involvement of, or is attributable to any neglect on the part of such person
a) Director
b) Manager
c) Secretary
d) All of the above
Answer
Answer: d) All of the above
99. If any person convicted of an offence under the Black Money Act is again convicted of an offence under any of the aforesaid provisions, he shall be punishable for the second and every subsequent offence with rigorous imprisonment of………………………
a) 3 years to 10 years
b) 6 months to 7 years
c) One year
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: a) 3 years to 10 years
100. If any person convicted of an offence under the Black Money Act is again convicted of an offence under any of the aforesaid provisions, he / it shall be liable to pay fine of ………………. for the second and every subsequent offence
a) Rs 1 lakh
b) Rs 10 lakhs
c) Rs 5 lakhs to 1 crore
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: c) Rs 5 lakhs to 1 crore
Black Money and Imposition of Tax Act 2015 MCQs – International Taxation
101. What is the mode of service of any notice, summons, requisition, order or any other communication under the Black Money Act?
a) By post
b) By email
c) By Approved courier service
d) All of the above
Answer
Answer: d) All of the above
102. What would be the address for service of any notice, summons, requisition, order or any other communication under the Black Money Act?
a) The address available in the PAN database of the addressee; or
b) The address available in the Aadhaar card
c) The address available in the return furnished under the Income-tax Act to which the communication relates
d) Both A and C
Answer
Answer: d) Both A and C
103. Which email address would be used for service of any notice, summons, requisition, order or any other communication under the Black Money Act?
a) Email address available in the return furnished under the Income-tax Act to which the communication relates
b) Email address of the company as available on MCA website
c) Any e-mail address made available by the addressee to the tax authority
d) All of the above
Answer
Answer: d) All of the above
104. When a notice, which is required to be served for the purpose of assessment under the Black Money Act, shall be deemed to be duly served upon a person
a) When assessee has appeared in any proceeding relating to assessment
b) When assessee has cooperated in any enquiry relating to assessment.
c) Both A and B
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: c) Both A and B
105. The amount of undisclosed foreign income and assets shall be rounded off to the nearest multiple of ………………….
a) Rs 10
b) Rs 100
c) Rs 5
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: b) Rs 100
106. The amount payable or receivable by the assessee under the Black Money Act shall be rounded off to the nearest multiple of ………………..
a) Rs 10
b) Rs 100
c) Rs 5
d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: a) Rs 10



