Country by Country Reporting (CbCR) Transfer Pricing
Generally, the group structure of a MNC would be as under : –
- Ultimate Parent company, say in USA;
- Regional Holding companies – Say one for Asia (Regional Holding company 1) which is a subsidiary of the US company and owns all the companies in Asia, one for Europe ( Regional Holding company 2) which is a subsidiary of the US company and owns all the companies in Europe ;
- Entity in respective countries like India owned by Regional Holding company of Asia , and Germany owned by Regional Holding company of Europe.
In some cases, due to large number of legal entities, the multinational enterprises structure intra company transaction within their group in such a manner , that higher profits are accrued in jurisdictions with low Tax rates , and lower profits are reported in jurisdictions with higher tax rate , even though the economic activity may not take place in the low tax jurisdictions. In order to obtain such information from the multinational enterprise, country by country regulations were introduced whereby a multinational enterprise is required to report certain Economic aspects relating to its business to the tax authorities , where country by country regulations exist.

Objectives of Country by Country Reporting
The key objectives of the Country by Country Reporting (CbCR) are as under: –
- The Report requires taxpayers to articulate consistent transfer pricing position, across the globe.
- The Report will provide tax administration with useful information to assess TP risk.
- It will facilitate tax administrations to determine about where their resources can most effectively be deployed, and in the event of audit, provide information to commence and targeted audit enquiries.
Background of Country by Country Reporting
- Section 92D of the IT Act requires maintenance of prescribed information and documents, relating to the international transactions and specified domestic transactions.
- The OECD report on Action Plan 13 of BEPS, provides for revised standards for transfer pricing documentation and a template for country-by-country reporting of income, earnings, taxes paid and certain measure of economic activity. It is recommended in the BEPS report, that the countries should adopt a standardized approach to transfer pricing documentation.
- Country-by-Country reporting mandates a three tiered structure of documentation at the group and local level.
Three Tier Structure of Documentation
Three-tiered structure of documentation as mandated by BEPS consists of : –
- a Master File containing standardized information relevant for all multinational enterprises (MNE) group members. It provides high level overview of group’s global business operations and global transfer pricing policies.
- a Local File referring specifically to material transactions of the local taxpayer; and
- a Country by Country report containing certain information relating to the global allocation of the MNE’s income and taxes paid, together with certain indicators of the location of economic activity within the MNE group.
Master File and Country by Country Reporting
- Section 286 of the IT Act requires Multinational Enterprises (MNEs) and Indian Multinational Enterprises to report annually CbC report for financial year 201617 and onwards.
- Rule 10DA lays down the procedure in relation to filing of Master file; and
- Rule 10DB lays down the procedure CbCR
Master File – Rule 10DA – Monetary Threshold For Maintenance of Master File
International group shall maintain information and documents in Master file when –
- Consolidated group revenue of the international group is more than Rs 500 crores (as reflected in Consolidated Financial Statements of the international group), and
- The aggregate value of international transaction –
-
- Is more than Rs. 50 crores during the accounting year as per books of account, or
- Is more than Rs. 10 crores in respect of purchase, sale, transfer, lease or use of intangible property.
Monetary Threshold For Maintenance of Master File

Master File [Rule 10DA]
Manner of Filling of Master File : –
a) Form 3CEAA for Master file :
The information of international group shall be furnished in master file in Form 3CEAA. Such form consists of two parts –
- Part A of Form 3CEAA : – It needs to be filed by every constituent entity of international group even if dual-threshold of group revenue (i.e., Rs 500 crores) and international transaction (i.e., Rs 50/10 crores) is not satisfied.
- Part B of Form 3CEAA : – It needs to be filed by constituent entity which satisfies the aforesaid condition of dual-threshold.
b) Form 3CEAB for intimation :
Where international group has more than one constituent entities resident in India, it should designate one of the entity for filing of master file in Form 3CEAA. In such case, Form 3CEAA has to be filed by such designated constituent entity and intimation of same should be filed in Form 3CEAB.
Manner of Filling of Master File

Master File Rule 10DA – Time limit For Filing of Master File in Form 3CEAA
Subject to Provision of Finance Bill 2018

Master File – Rule 10DA – Information to be maintained for Master File
Key information and documents required for Master File includes –
- Description of function, asset and risk analysis (“FAR”) of all the constituent entities that contribute atleast 10% of the revenue or assets or profits of the group.
- Description of financial arrangement of the group including names and address of top ten unrelated lenders.
- List of all entities of international group which are engaged in development and management of intangible property.
Country by Country Report – Rule 10DB
Monetary Threshold for maintenance of Country by Country Report : –
As per Rule 10DB, where the consolidated group revenue of international group exceeds Rs 5500 crores for filing of Country-by-Country report.
Intimation in Form 3CEAC : –
Indian entity, having a parent entity resident outside India, will be required to provide information on or before the prescribed date in Form 3CEAC :-
a. Whether it is an alternate reporting entity of the international group; or
b. The details of the parent entity or the alternate reporting entity, if any of the international group, and the country of territory of which the said entities are resident.
Manner and due date of filing of Country by Country Report
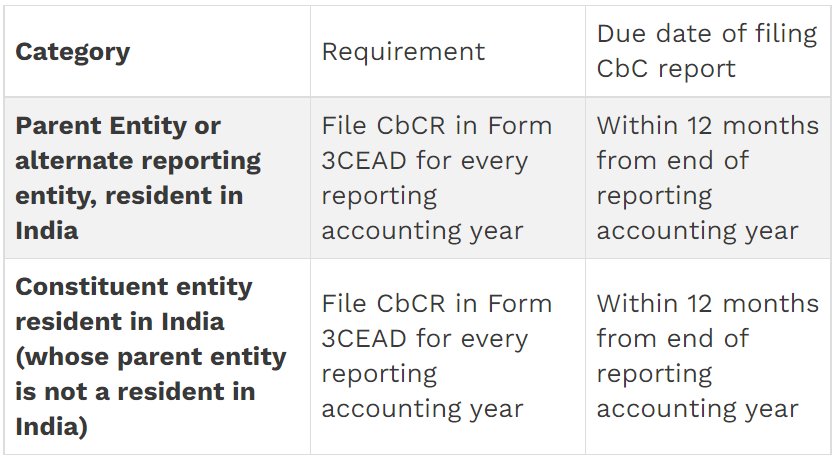
Note :- Constituent entity resident in India (whose parent entity is not resident in India) needs to submit intimation in Form 3CEAC to specify whether it is alternate reporting entity of the group or details of parent entity, etc. Form 3CEAC should be filed at least two months before the due date of furnishing of CbCR.
CBC Reporting by Indian Entity where it is Member of International Group
a) A resident constituent entity of an International group shall be required to furnish CbC report to the prescribed authority, if the parent entity of the group is resident :
- In a country with which India does not have an arrangement for exchange of the CbC report; or
- Such country is not exchanging information with India even though there is an agreement (i.e. existence of systematic failure); and
- This fact has been intimated to the entity by the prescribed authority.
b) In case where more than one Indian resident entities are constituents of international group, the report shall be furnished by the entity, which is nominated by the international group (provided information of such nomination has been conveyed to prescribed authority in writing on behalf of the group).
Safeguards to Avoid Duplication
- An entity in India is not required to furnish CbC report, if following conditions are satisfied:
a) an alternate reporting entity of the international group has furnished report with the tax authority of the country or territory in which such entity is resident on or before the date specified;
b) the report is required to be furnished under the law for the time being in force in the said country or territory;
c) the said country or territory has entered into an agreement with India providing for exchange of the CbC report;
d) the prescribed authority has not conveyed to entity of the group that is resident in India, any systemic failure in respect of the said country or territory;
e) the alternate reporting entity informed in writing to the said country or territory on behalf of the international group; and
f) the prescribed authority has been informed by the entities in India
Non-Compliance with CBC Provisions
Penalty for Non Furnishing of Report : –
Where an entity which is required to furnish report under CbC provisions, fails to do so within the prescribed time, penalty shall be payable –
- At Rs. 5,000 per day where period of default is less than a month, or
- At Rs. 15,000 per day where default period exceeds a month, or
- At Rs. 50,000 per day in case of continuing default even after service of order levying penalty.
Penalty for failure to produce information and documents: –
In case information called by prescribed authority for determination of accuracy of CbC report is not submitted within the time specified in the notice, reporting entity shall be penalized by Rs 5,000/- per day after expiry of the period specified in such notice.
Further, for any default that continues even after service of order levying penalty, then penalty for default beyond date of service of penalty order shall be Rs 50,000/- per day
Penalty for filing of inaccurate information in CBC report
If an entity has provided any inaccurate information in the CbC report, penalty would be Rs. 500,000/- if
- The entity has the knowledge of the inaccuracy at the time of furnishing the report but does not inform the prescribed authority; or
- The entity discovers the inaccuracy after the report is furnished and fails to inform the prescribed authority and furnish correct report within a period of 15 days of such discovery; or
- The entity furnishes inaccurate information or document in response to notice of the prescribed authority.
Exemption from penalty : –
Section 273B provides for non-levy of penalty u/s 271GB if the assessee proves that there was reasonable cause for such failure.
Maintenance and Furnishing of Master File
Penalty for non-furnishing of information and documents to the prescribed authority u/s 286(1) shall be Rs. 5,00,000.
Note :- There shall be no penalty if there is any reasonable cause for non-furnishing of information and documents to the prescribed authority.
Definitions of various terms used in this chapter
Definition of “International Group”
It means any group that includes,
- two or more enterprises which are resident of different countries or territories; or
- an enterprise, being a resident of one country or territory, which carries on any business through a permanent establishment in other countries or territories;
Definition of Group
“Group” includes a parent entity and all the entities in respect of which, for the reason of ownership or control, a consolidated financial statement for financial reporting purposes,
- is required to be prepared under any law for the time being in force, or as per the accounting standards of the country or territory of which the parent entity is resident; or
- would have been required to be prepared had the equity shares of any of the enterprises were to be listed on a stock exchange in the country or territory of which the parent entity is resident.
Definition of Constituent Entity
“Constituent Entity” means,
- any separate entity of an international group that is included in the consolidated financial statement of the said group for financial reporting purposes, or may be so included for the said purpose, if the equity share of any entity of the international group were to be listed on a stock exchange;
- any such entity that is excluded from the consolidated financial statement of the international group solely on the basis of size or materiality; or
- any permanent establishment of any separate business entity of the international group included in clause (i)* or clause (ii)*, if such business unit prepares a separate financial statement for such permanent establishment for financial reporting, regulatory, tax reporting or internal management control purposes
Definition of Parent Entity
“Parent Entity” means a constituent entity, of an international group holding, directly or indirectly, an interest in one or more of the other constituent entities of the international group, such that,
- it is required to prepare a consolidated financial statement under any law for the time being in force or the accounting standards of the country or territory of which the entity is resident; or
- it would have been required to prepare a consolidated financial statement had the equity shares of any of the enterprises were listed on a stock exchange,
and, there is no other constituent entity of such group which, due to ownership of any interest, directly or indirectly, in the first mentioned constituent entity, is required to prepare a consolidated financial statement, under the circumstances referred to in clause (i) or clause (ii), that includes the separate financial statement of the first mentioned constituent entity
Definition of Reporting Entity
“Reporting Entity” means
- the constituent entity including
- the parent entity, or
- the alternate reporting entity,
- that is required to furnish a report as per CbC reporting provisions.
Definition of Alternate Reporting Entity
“Alternate Reporting Entity” means
- any constituent entity of the international group
- that has been designated by such group, in the place of the parent entity,
- to furnish the report of the nature referred to in sub-section (2)
- in the country or territory in which the said constituent entity is resident on behalf of such group;
Definition of Systematic Failure
“Systemic Failure” with respect to a country or territory means that the country or territory has an agreement with India providing for exchange of report of the nature referred to in sub-section (2), but
- in violation of the said agreement, it has suspended automatic exchange; or
- has persistently failed to automatically provide to India the report in its possession in respect of any international group having a constituent entity resident in India.
Definition of Accounting Year
“Accounting Year” means,
- a previous year, in a case where the parent entity or alternate reporting entity is resident in India; or
- an annual accounting period, with respect to which the parent entity of the international group prepares its financial statements under any law for the time being in force or the applicable accounting standards of the country or territory of which such entity is resident, in any other case.
Definition of Agreement
“Agreement“ means
- an agreement referred to in section 90(1) or section 90A(1); or
- any agreement as may be notified by the Central Government in this behalf.
Definition of Consolidated Financial Statement
“Consolidated Financial Statement” means the financial statement of an international group in which the assets, liabilities, income, expenses and cash flows of the parent entity and the constituent entities are presented as those of a single economic entity.
Country by Country Reporting Transfer Pricing Topics Covered: –
- Objective of Country by Country reporting (CbCR).
- Background of CbCR
- Applicability of CbCR
- Safeguards to avoid Duplicity
- Non-compliance with CbCR provisions
- Definitions of various terms used in this chapter
For any queries, please write them in the Comment Section or Talk to our tax expert



