MISCELLANEOUS PROVISIONS FOR NON-RESIDENTS
Under the provision of Section 139, following person are mandatorily required to file return of income : –
- Company or firm ; or
- A person other than a company [or a firm], if his total income or the total income of any other person in respect of which he is assessable under this Act during the previous year exceeded the maximum amount which is not chargeable to income-tax.
Every non-resident is also required to file return of income, in respect of income deemed to accrue or arise in India u/s 9(1).However, it shall not be necessary for a non-resident Indian to furnish a return of his income u/s 139(1) if —
- his total income consisted only of investment income or income by way of long-term capital gains or specified interest and dividend; and
- the tax deductible at source has been deducted from such income.
Besides this, there are several other provision which contains similar provision, wherein if the non-resident derives certain specific incomes , which are generally chargeable to Tax at a flat rate, and the requisite TDS thereon has been deducted, the non-resident is exempted from filing return of income in India.
DUE DATE OF FILING RETURN OF INCOME [SECTION 139]
The due date of filing return of income in the case of various assessees including the non-residents are as under : –
![DUE DATE OF FILING RETURN OF INCOME [SECTION 139]](https://sortingtax.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/DUE-DATE-OF-FILING-RETURN-OF-INCOME-SECTION-139.png)
WHO IS REPRESENTATIVE ASSESSEE ? [SECTION 160]
In certain cases, a non-resident may derive certain income from India, however, they do not have any physical presence in India. In such cases, if the non-resident does not pay the tax liability, it is very difficult for the Indian government to track such non-residents and recover the tax payable by them. To do with such cases, the law provides that certain persons would be treated as agent of non-resident in India. Generally, the person who has a business relation with non-resident, or are liable to make some payments to the non-resident, are considered as the agent of non-resident in India. The impact of this is, that in case the non-resident does not discharge their tax liability, the tax office can recover the tax demand from such person who are treated as agents of non-residents in India.
Section 9(1) specifies cases wherein income of non-resident shall be deemed to accrue or arise in India.“Representative assessee” , in respect of the income of a non-resident specified in Section 9(1), means the agent of the non-resident, including a person who is treated as an agent under Section 163 .Every representative assessee shall be deemed to be an assessee for the purposes of the IT Act [Section 160(2)]
WHO MAY BE REGARDED AS AGENT OF NON-RESIDENT ? [SECTION 163]
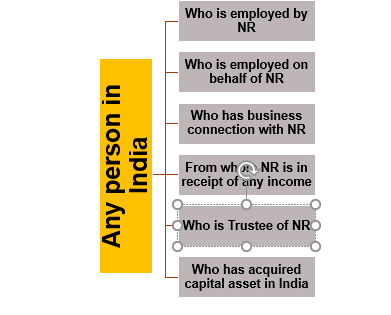
Agent”, in relation to a non-resident, includes any person in India : –
- Who is employed by non-resident [i.e., Any employee in India of such non-resident]; or
- Who is employed by any other person on behalf of the non-resident ; or
- who has any business connection with the non-resident . “Business connection” shall have the meaning assigned to it in Explanation 2 to section 9(1) of the IT Act . OR
- from or through whom the non-resident is in receipt of any income, whether directly or indirectly. For EXAMPLE : – Indian resident who is paying royalty/FTS to non-resident would be treated as agent of such non-resident
- who is the trustee of the non-resident;and
- Includes any other resident or non-resident, who has acquireda capital assetin India, by means of a transfer from such non-resident.Any person who has acquired capital asset in India via gift, will, etc.( and under any other circumstance specified u/s 47) shall not be regarded as agent .
However, it may be noted that no person shall be treated as the agent of a non-resident , unless he has had an opportunity of being heard by the Assessing Officer as to his liability to be treated as such.
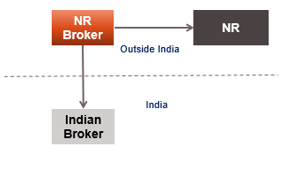
BROKER MAY NOT BE REGARDED AS AGENT ? [SECTION 163]
A broker in India who, does not deal directly with or on behalf of a non- resident principal, but deals with or through a non-resident broker shall not be deemed to be an agent, if the following conditions are fulfilled, namely:—
- the transactions are carried on in the ordinary course of business through the first-mentioned broker; and
- the non-resident broker is carrying on such transactions in the ordinary course of his business and not as a principal.
LIABILITY OF REPRESENTATIVE ASSESSEE – SECTION 161
Every representative assessee shall be subject to the same duties, responsibilities and liabilities as if the income were income received by or accruing to or in favour of him beneficially.
He shall be liable to assessment in his own name in respect of that income but any such assessment shall be deemed to be made upon him in his representative capacity only ;
The tax shall, be levied upon and recovered from him in like manner and to the same extent as it would be leviable upon and recoverable from the person represented by him .
NOTE : –
Where any person is assessable under this Chapter in the capacity of a representative assessee, he shall not, in respect of that income, be assessed under any other provision of the IT Act .
RIGHT OF REPRESENTATIVE ASSESSEE TO RECOVER TAX PAID – SECTION 162
Representative assessee has the following rights : –
- RIGHT TO RECOVER TAXES PAID : –
Every representative assessee who paysany sum(i.e., income-tax, interest, penalty, etc.) under the IT Act shall be entitled to recover the sum so paid from the person on whose behalf it is paid .
- RIGHT TO RETAIN TAXES PAID : –
Every representative assessee who pays any sum(i.e., income-tax, interest, penalty, etc.) under the IT Act shall be entitled to retain out of any moneys that may be in his possession [or may come to him] in his representative capacity, an amount equal to the sum so paid.
- RIGHT TO RETAIN ESTIMATED TAXES : –
Any representative assessee, may retain out of any money payable by him to the person on whose behalf he is liable to pay tax (i.e., principal), a sum equal to his estimated liability under the IT Act.
- RIGHT TO OBTAIN CERTIFICATE FROM AO
In the event of any disagreement between the principal and such representative assessee as to the amount to be so retained, such representative assessee may secure from the Assessing Officer a certificate stating the amount to be so retained pending final settlement of the liability, and the certificate so obtained shall be his warrant for retaining that amount .
The amount recoverable from such representative assessee or person at the time of final settlement shall not exceed the amount specified in such certificate . However, when representative assessee holds any additional assets of the principal at the time of final settlement, the AO may initiate recovery of the balance tax liability of the principal to the extent of such additional assets of the principal .
DIRECT ASSESSMENT OR RECOVERY NOT BARRED – SECTION 166
The Provisions of the IT Act relating to the representative assessee shall not prevent either –
- the direct assessment of the person on whose behalf or for whose benefit income is receivable, or
- the recovery from such person of the tax payable in respect of such income .
REMEDIES AGAINST PROPERTY IN CASES OF REPRESENTATIVE ASSESSEES – SECTION 167
Where any demand is raised by the Assessing Officer, whether against the
representative assessee or directly against the beneficiary , the AO shall have the same remedies against all property vested in or under the control or management of any representative assessee, as he would have against the property of any person liable to pay any tax .
RECOVERY OF TAX IN RESPECT OF NON-RESIDENT FROM HIS ASSETS – SECTION 173
Where a non-resident is entitled to deemed income referred to in Section 9(1)(i), the tax chargeable on such income, whether in his name or in the name of a representative assessee, may be recovered by way of deduction under any of the provisions of Chapter XVII-B.
Further, any arrears of tax may be recovered also in accordance with the provisions of the IT Act , from any assets of the non-resident which are in India, or may at any time come, within India.
RECOVERY OF TAX IN RESPECT OF NON-RESIDENT FROM HIS ASSETS LOCATED IN INDIA – SECTION 173
Where an assessee is in default or is deemed to be in default in making a payment of tax, the Tax Recovery Officer may, if the assessee has property in a country outside India*, forward to the CBDT, a certificate drawn up by him u/s 222 and CBDT may take such action thereon as it may deem appropriate having regard to the terms of the agreement with such country.
* Being a country with which the Central Government has entered into an agreement for the recovery of income-tax under the IT Act and the corresponding law in force in that country.
RECOVERY OF TAX IN RESPECT OF NON-RESIDENT FROM HIS ASSETS LOCATED OUTSIDE INDIA – SECTION 173
Where the Government of any country outside India* has to recover any taxes from a property of a taxpayer, which is located in India, such Government may send a certificate for the recovery of any tax due under such corresponding law of that Country to CBDT . On receipt of such certificate the CBDT may forward such certificate to any Tax Recovery Officer , within whose jurisdiction such property is situated and thereupon such Tax Recovery Officer shall –
- proceed to recover the amount specified in the certificate in the manner specified in a certificate drawn up by him u/s 222 ; and
- remit any sum so recovered by him to the Board after deducting his expenses in connection with the recovery proceedings.
*Where an agreement is entered into by the Central Government with the Government of any country outside India for recovery of income-tax under the IT Act and the corresponding law in force in that country
TAXATION OF LIAISON OFFICE
Where a non-resident has a liaison office in India,which is set up in accordance with the RBI guidelines, such non-resident shall file a annual statement in Form 49C to the Assessing officer in respect of its activities in a financial year. Such statement in Form 49C shall be submitted within 60 days from the end of such financial year .Such annual statement shall be duly verified by the Chartered Accountant or the person authorised in this behalf by the non-resident person, who shall be known as the Authorised Signatory .The annual statement referred to in sub-rule (1) shall be furnished in electronic form along with digital signature.
LIAISON OFFICE MEANS
A place of business to act as
- A channel of communication between the principal place of business or head office and entities in India ;
- but which does not undertake any commercial activity and
- Maintains itself out of inward remittances received from abroad through normal banking channel.
For any queries, please write them in the Comment Section or Talk to our tax expert




