EXEMPT INCOME OF NON-RESIDENTS – The tax exemptions available to various incomes of a non-resident under Section 10 of the Income Tax Act are discussed as under : –
INTEREST INCOME FROM NOTIFIED SECURITIES AND BONDS – SECTION 10(4)(i) OF INCOME TAX ACT
Any income by way of interest on specified securities and bonds, payable to a non-resident, will be exempt from tax. Such specified securities and bonds, should be notified by the Central Government.
NOTES :
- Income by way of premium on redemption of such bonds is also exempt from tax.
- This exemption is not available in respect of any further issue of bonds or securities on or after the 1.6.2002.
- Government has specified 4 1/4 per cent. National Defence Loan, 1968. and 4 3/4 per cent. National Defence Loan, 1972, for the purpose of Section 10(4)(i) vide Notification No. S.O. 3331, dated 19-10-1965.
INTEREST INCOME EARNED IN NRE ACCOUNT – SECTION 10(4)(ii)
Any interest income of an individual on credit balance in a Non-resident (External) Account (NRE A/c) in any bank in India, shall be exempt . However, such credit should have been made accordance to the Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 (FEMA, 1999), and the rules made under FEMA, 1999.
Such exemption is available only when any of the following conditions are satisfied: –
- Such individual is a person resident outside India, as defined in FEMA, 1999, or
- Such person has been permitted by the Reserve Bank of India to maintain such account.
POINTS TO CONSIDER
As per Section 2 of FEMA, Person Resident Outside India means a person who is not resident in India. Further, Person resident in India means a person residing in India for more than 182 days during the course of the preceding financial year.
However, it does not include a person who has gone out of India or who stays outside India, for
- Taking up employment outside India, or
- Carrying on outside India a business or vocation outside India, or
- Any other purpose, in such circumstances as would indicate his intention to stay outside India for an uncertain period
- Interest income earned on money standing to Non-resident Ordinary (NRO) account of non-resident is not eligible for exemption.
Interest on NRO Account – Interest income earned on money standing to Non-resident Ordinary (NRO) account of non-resident is not eligible for exemption.
In case of Joint holders of NRE Accounts, the joint holders would not constitute an AOP by merely having these accounts in joint names and benefit of exemption will be available to them subject to fulfillment of other conditions of the individual holders – CBDT Circular No. 592 dated February 4, 1991.
EXAMPLE 1 : –
Mr. Abhay, is UK resident since 2001, and did not visit India since 2001. He holds an Non-resident (External) Account with ABC Bank, New Delhi Branch. Interest of Rs. 50,000 was credited to such account during financial year 2019-20 on credits made as per FEMA 1999. Whether such interest income would be exempt?
SOLUTION : –
Interest income earned by Person Resident outside India, on money credited in Non-resident (External) Account shall be exempt from tax under Section 10(4)(ii) of Income Tax Act.
Abhay did not stay in India for a single day during preceding FY (i.e., FY 2018-19). He is person resident outside India, and shall be exempt from income-tax on such interest income for A.Y 2020-21 u/s 10(4)(ii).
EXAMPLE 2 : –
Sita and Gita are joint holders of Non-resident (External) Account in an Indian Bank. Both of them were residents of UK since 2005. They did not visit India since 2004. They earned interest of Rs 1,00,000 during financial year 2019-20 on such account on credits permissible as per FEMA 1999. Whether such interest income would be exempt , or taxable as income of AOP, or taxable as their respective income in their hands?
SOLUTION : –
CBDT has clarified that joint holders of the NRE Accounts, do not constitute an AOP by merely having these accounts in joint names. Since both Sita and Gita are person resident outside India, interest income earned in joint NRE account would be exempt from tax in the hands of Sita and Gita in their individual capacity for A.Y 2020-21 u/s 10(4)(ii).
EXAMPLE 3 : –
Mr. Shyam, is resident of USA since 2001. He holds an NRO account with ABC Bank, New Delhi Branch. Interest of Rs 1,00,000 was credited to such account during financial year 2019-20. Whether such interest income would be exempt?
SOLUTION : –
Interest income earned by Person Resident outside India on money credited in NRE account shall be exempt from tax under Section 10(4)(ii). In this case, interest was earned on money standing to the credit in NRO account and not NRE account. Thus, Shyam cannot claim exemption from income-tax on interest income on NRO A/c for A.Y 2020-21.
INTEREST ON SAVINGS CERTIFICATES – SECTION 10(4B)
Interest received by a non-resident individual, who is the original subscriber of certain saving certificates , would be exempt from tax provided : –
- Individual is either a Citizen of India or a person of Indian origin;
- Saving certificates were issued before 1.6.2002 by the Central Government and notified by it in the Official Gazette.
NOTES :
- In order to claim such exemption, the individual should have subscribed to such certificates in convertible foreign exchange remitted from a country outside India in accordance with the provisions of the FEMA, 1999 and any rules made thereunder.
- As per Explanation to Section 115C, a person shall be deemed to be of Indian origin if he, or either of his parents or any of his grand-parents, was born in undivided India.
INTEREST ON RUPEE DENOMINATED BONDS – SECTION 10(4C)
Any income by way of interest payable by any Indian company or business trust , to a non-resident, in respect of monies borrowed from a source outside India by way of issue of rupee denominated bond, before the 1st day of July, 2020. This provision is effective from 1.4.2019, and shall be considered accordingly.
(4D) Exemption u/s 10(4D) is available when the following conditions are satisfied : –
- Any income accrued or arisen to, or received to a specified fund
- Income arises from transfer of capital asset referred to in clause (viiab) of section 47, on a recognized stock exchange located in any International Financial Services Centre and consideration for such transaction is paid or payable in convertible foreign exchange.
Such exemption is available to the extent income from transfer of specified capital in respect of units held by a non-resident.
Explanation.—For the purposes of this clause, the expression —
(a) “convertible foreign exchange” means foreign exchange which is for the time being treated by the Reserve Bank of India as conver-tible foreign exchange for the purposes of the Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 (42 of 1999) and the rules made thereunder;
(b) “manager” shall have the meaning assigned to it in clause (q) of sub-regulation (1) of regulation 2 of the Securities and Exchange Board of India (Alternative Investment Fund) Regulations, 2012, made under the Securities and Exchange Board of India Act, 1992 (15 of 1992);
(c) “specified fund” means a fund established or incorporated in India in the form of a trust or a company or a limited liability partnership or a body corporate,—
(i) which has a certificate of registration as a Category III Alternative Investment Fund and is regulated under the Securities and Exchange Board of India (Alternative Investment Fund) Regulations, 2012, made under the Securities and Exchange Board of India Act, 1992 (15 of 1992);
(ii) such fund is located in any International Financial Services Centre;
(iii) of which all the units are held by non-residents other than units held by a sponsor or manager;
(d) “sponsor” shall have the meaning assigned to it in clause (w) of sub-regulation (1) of regulation 2 of the Securities and Exchange Board of India (Alternative Investment Fund) Regulations, 2012, made under the Securities and Exchange Board of India Act, 1992 (15 of 1992);
(e) “trust” means a trust established under the Indian Trusts Act, 1882 (2 of 1882) or under any other law for the time being in force;
(f) “unit” means beneficial interest of an investor in the fund and shall include shares or partnership interests;
REMUNERATIONRECEIVED BY OFFICIALS OF EMBASSIES, HIGH COMMISSION OF FOREIGN STATES – SECTION 10(6)(ii)
Where a person serves as an official (including a person who is a member of staff of any of these official) of an embassy, high commission, legation, commission, consulate or trade representation of foreign state, there remuneration shall be exempt from tax under Section 10(6)(ii) of Income Tax Act.
In order to claim such exemption , all of the following conditions should be satisfied by such person : –
i) Recipient should not be a citizen of India although such individual could be a person of Indian origin.
ii) Remuneration of Corresponding Indian Government official, in the foreign country should also enjoy similar exemption.
iii) Such officers should not engage in any other business or profession or employment in India.
EXAMPLE 1 : –
Examine the taxability of the following person for the purpose of Section 10(6)(ii) : –
a) Rohit, is a citizen of India but a tax resident of UK since 2010. He was appointed as a senior official of the UK embassy in India, and earned a remuneration of Rs. 20 lakhs during FY 2019-20. Whether his salary income earned in India would be exempt u/s 10(6)(ii) ?
b) Ramesh was born in India, but currently he is a resident and Citizen of only UK. He was appointed as a senior official of the UK embassy in India. He earned a remuneration of Rs 30 lakhs during FY 2016-17. Government officials of Indian embassy in UK also enjoys similar exemption. Ramesh is not engaged in other business or profession or employment in India. Whether remuneration of Mr. Ramesh would be taxable in India?
c) Garry, a UK Citizen but currently a resident of Australia, was appointed as a senior official of the Australian embassy in India. He earned a remuneration of Rs 15 lakhs during FY 2016-17. Whether such remuneration would be exempt in his hands for AY 2017-18, considering he is a citizen of UK, and not Australia ?
SOLUTIONS : –
a) Exemption under Section 10(6)(ii) of Income Tax Act is available only for person who is not a citizen of India. Mr. Rohit cannot avail tax exemption on his remuneration of Rs. 20 lakhs as he is a citizen of India.
b) Person of Indian origin can claim exemption u/s 10(6)(ii) , when he is not a citizen of India. Mr. Ramesh is a person of Indian origin. However, he is an Individual who is not a citizen of India. He also fulfills the following other conditions of the Section 10(6)(ii) :
- Remuneration of Indian embassy official also enjoy similar tax exemption in foreign country
- Such Government official is not engaged in any other business or profession or employment in India.
Accordingly, remuneration of Rs. 30 lakhs shall be exempt in his hands.
c) Remuneration of Rs. 50 lakhs shall be exempt in the hands of Mr. Garry if he satisfies other conditions of Section 10(6)(ii).
REMUNERATION OF FOREIGN EMPLOYEE – SECTION 10(6)(vi) (SOMETIMES CALLED SHORT STAY EXEMPTION)
In many cases, a non-resident who carries on business in India, may send some employees to India. As discussed earlier, income from salary, for which services have been rendered in India is liable to tax in India. In such a case, even though these employees may come to India for a small number of days, they would be liable to pay taxes on salary income in India. Further, if the income of the non-resident employer is liable to tax in India, the employee would be able to claim a deduction of such salary against it’s taxable income in India.
In order to ensure, that employees who do not visit India beyond a particular threshold number of days, are not burdened with payment of taxes and undertaking compliances, this section provides for exemption of tax on such employees. However, to ensure that the Indian government does not lose tax revenue due to such salary been claimed as an expense by the employer, the corresponding deduction in such a case is also denied to the employer.
Section 10(6)(vi) provides that remuneration received by a foreign national as an employee of a foreign enterprise, for services rendered by him during his stay in India is exempt from tax, provided all the following conditions are satisfied :
i) Employee is an individual who is foreign citizen, and not a citizen of India;
ii) The foreign enterprise is not engaged in any business or trade in India;
iii) The employee’s total stay in India is not more than 90 days (i.e., 90 days or less) in such previous year ; and
iv) Employee’s remuneration is not liable to be deducted from the income of the foreign employer chargeable under the IT Act.
EXAMPLE 1 : –
Mr. Haria is a citizen of India but resident of UK since 2010. He was appointed as an employee of a UK enterprise for their project in India. Such UK enterprise is not engaged in any business in India. During FY 2019-20, Haria earned a remuneration of Rs 20 Lakhs for his India related assignment. His stay in India in aggregate was 85 days. Further such UK enterprise has not claimed any deduction of such remuneration in computing its income under the IT Act of India. Whether remuneration of Harry is exempt from tax in India ?
SOLUTION : –
Since Haria is a Citizen of India, he cannot claim exemption under Section 10(6)(vi) of Income Tax Act even if he satisfies the other three conditions of exemption.
EXAMPLE 2 : –
Examine the claim of exemption u/s 10(6)(vi) in following scenarios : –
- When Haria is a citizen of UK [All other facts remain same]
- When Haria is a resident of UK and he stays in India for 120 days during FY 2019-20 [All other facts remain same]
- When Haria is a resident of UK and remuneration paid to him is borne by PE of foreign enterprise in India. [All other facts remain same]
SOLUTION : –
- As Haria is not a citizen of India, he can claim exemption.
- One of the conditions to claim exemption u/s 10(6)(vi) is that the stay of foreign employee should not be more than 90 days in India. Haria cannot claim exemption as his stay in India was more than 90 days.
- While computing the taxable income of Indian PE of foreign enterprise, the expenses incurred by PE is deductible. Thus, if the salary has been borne by PE, it would have been deducted while calculating the taxable income of Indian PE (given that it is borne by the PE). Haria would not be eligible to claim exemption as one of the condition to claim exemption is not satisfied.
EMPLOYMENT OF NON-CITIZEN ON A FOREIGN SHIP – SECTION 10(6)(viii)
Where a foreign citizen works as a crew of a foreign ship under an employment , his remuneration would be exempt from tax , if his total stay in India is not more than 90 days (i.e., 90 days or less) during the previous year.
In other words the following conditions would need to be satisfied to claim the exemption : –
- The individual should be a foreign citizen ;
- He should have employment and the remuneration should be derived as a part of his employment ;
- The total stay in India should not be more than 90 days during the previous year ; and
- He should be working as a member of foreign ship.
REMUNERATION OF FOREIGN GOVERNMENT EMPLOYEE FOR SPECIFIED TRAINING – SECTION 10(6)(xi)
Any remuneration received by an employee of Government of foreign state during his stay in India shall be exempt from tax, if all of the following conditions are satisfied.
i. Remuneration should be received in connection with training in any establishment , or office of, or in any undertaking owned by –
a) the Government of India, or
b) Any company owned by the Central Government or any State Government
c) Any company which is subsidiary of a company owned by Central/ State Government, or
d) Any statutory corporation; or
e) any society registered under Societies Registration Act, 1860 or under any law and wholly financed by the Central Government or any State Government.
ii. Employee is an individual who is not a citizen of India (i.e., he should be a foreign citizen).
TAX PAID BY GOVERNMENT OR INDIAN CONCERN ON ROYALTY OR FEES FOR TECHNICAL SERVICES DERIVED BY FOREIGN COMPANIES – SECTION 10(6A)
In certain cases, Foreign companies or Enterprise, who provide certain services to an Indian company or the Government, may enter into a contract, whereby the Indian tax liability on the revenue derived by them by way of royalty of fee for Technical Services, is to be Borne by the payor. In such cases, even the Tax amount which is Borne by the payor is considered as income of the foreign company in the absence of any specific exemption. Therefore the tax payable on such income is calculated by grossing up the net amount payable to the foreign company with the applicable tax rate.
Section 10(6A) provides that in certain cases, the tax paid by the Government or an Indian concern on royalty or fees for technical services derived by foreign enterprise shall be exempt from tax. In such cases, the tax amount would be calculated by applying the relevant rate to the gross royalty or Fee for Technical Services, i.e tax will not be grossed up with the income of foreign company.
Such exemption is available when all the following conditions are satisfied:
- Recipient of income is a foreign company ;
- It earns income by way of royalty or fees for technical services ;
- Such royalty or fees for technical services is received from Government or Indian Concern ;
- Such payment is made in pursuance of an agreement which is approved by Government of India and entered into after May 31, 1976 but before 1-6-2002, or such agreement is in accordance with the Industrial policy of the Government, even if it is not approved by the Government
If all of the above conditions are not satisfied, the exemption would not be available.
Let us look at an example to understand this point better : –
EXAMPLE 1 : –
Moon India Private Limited (MIPL) has to pay royalty of Rs 18 lakh to Sun Inc. As per the agreement of MIPL with Sun Inc., Indian withholding Taxes (assuming 10%) would be borne by the MIPL. Such agreement is not in accordance with industrial policy of the Government.
Compute –
- The amount of Indian taxes borne by MIPL (excluding Surcharge and Cess), and
- The total income of Sun Inc.?
SOLUTION : –
Royalty agreement is neither approved by the Government nor in accordance with the industrial policy of the Government Thus, taxes borne by Moon India, would be income in the hands of Sun Inc. As taxes borne by Moon India is not exempt in the hands of Sun Inc –
i) There will be grossing up while calculating the amount of withholding tax of Sun Inc.
ii) Withholding tax (i.e., taxes borne by Moon India) would be included in the total income of Sun Inc
Part A : –
Moon India has to bear withholding tax of Rs 200,000 [(18 lakh/90%)*10%] on behalf of Sun Inc. Since the withholding tax rate is 10%, the actual payment made to the foreign company would be 90% of the gross amount and hence Rs. 18 lakh have been divided by 90..
Part B : –
Total income of Sun Inc. would be Rs 20,00,000 (18,00,000 + 2,00,000) as such tax payments would be included in the total income of Sun Inc.
TAX ON OTHER INCOME DERIVED BY NON-RESIDENT NON CORPORATE ASSESSEE/ FOREIGN COMPANIES – SECTION 10(6B)
In certain cases, Foreign companies or Enterprise, who earn income other than royalty or fee for technical services from an Indian company or the Government, may enter into a contract, whereby the Indian tax liability on the revenue derived by them, is to be Borne by the payor. In such cases, even the Tax amount which is Borne by the payor is considered as income of the foreign company.
Section 10(6A) provides that in certain cases, the tax paid by the Government or an Indian concern on income other than Salary, or royalty or fees for technical services, which is derived by foreign enterprise shall be exempt from tax. In such cases, the tax amount would be calculated by applying the relevant rate to the gross receipts i.e tax will not be grossed up with the income of foreign company.
Such exemption is available when following conditions are satisfied : –
- Recipient of income is a non-resident
- It has any income (other than Salary, Royalty or fees for technical services)
- Such income is received from Government or Indian Concern
- Such payment is made in pursuance of agreement made before 1-6-2002 by the Indian Government with foreign Government or international organization or any related agreement approved by Indian Government before 1-6-2002.
TAX ON INCOME FROM LEASING OF AIRCRAFT ETC. DERIVED BY FOREIGN COMPANIES – SECTION 10(6BB) OF INCOME TAX ACT
Tax paid by an Indian concern, which is engaged in operation of aircraft , for payment of lease charges/rental for an aircraft or engine of aircraft , to foreign Government or foreign enterprise shall be exempt from tax.
Such exemption is available when following conditions are satisfied:
- Recipient of income is either a foreign enterprise or foreign Government
- It has income by way of lease for aircraft or engine of aircraft
- Such income is received from an Indian company engaged in the operation of aircraft. Income from any other enterprise shall not be eligible for exemption.
- Receipts are other than payment for providing spares or services in connection with the operation of leased aircraft
- Payment is made under an agreement entered into after 31-3-1997 but before 1-4-1999 or agreement is entered into after 31-3-1997 and approved by the Indian Government.
ROYALTY OR FTS FOR PROJECTS CONNECTED WITH INDIAN SECURITY – SECTION 10(6C) OF INCOME TAX ACT
Income by way of royalty or Fees for technical services, which is derived by a foreign company (so notified by Central Government) , shall be exempt from tax , where such payment is made under an agreement with Indian Government . Such services may be provided in or outside India, but should be made in connection with projects connected with security of India.

ROYALTY AND FTS PAYMENT BY NTRO TO A NON-RESIDENT TO BE TAX-EXEMPT – SECTION 10(6D)– INSERTED BY THE FINANCE ACT 2018
The following income arising to foreign company or non-corporate non-resident shall be exempt from tax:-
a) Income by way of royalty from the National Technical Research Organisation (NTRO), or
b) Fees for technical services rendered in or outside India to, the NTRO.
Consequently, NTRO will not be required to deduct tax at source on such payments.
INCOME OF AN INDIVIDUAL TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE PROGRAMMES – SECTION 10(8)
Income of an individual serving in India in connection with any co-operative technical assistance programme shall be exempt from tax provided : –
- Remuneration is received by the individual directly or indirectly from the Foreign Government ; and
- Any other income of the individual which accrues or arises outside India, and is not deemed to accrue or arise in India, shall also be exempt provided that such individual is required to pay income tax to the foreign Government
For taxability of income of family member of such employee, refer para <>.
REMUNERATION OF CONSULTANT / THEIR FOREIGN EMPLOYEES AND FAMILY MEMBERS – SECTION 10(8A) OF INCOME TAX ACT
Under this Section, the following three type of payment would be covered : –
- Remuneration of a consultant
- Remuneration of an employee of the consultant
- Income of the family members of the consultant
Each of these three are discussed as under : –
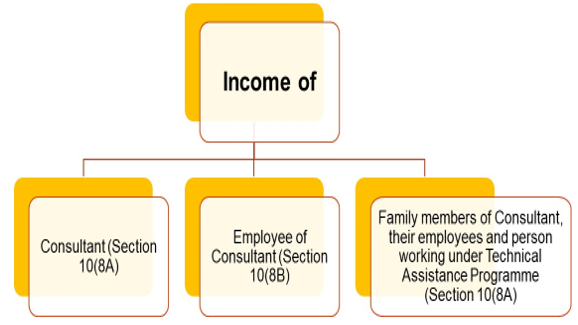
A. Remuneration of consultant – Section 10(8A) : –
As per Section 10(8A), following incomes of consultant are exempt from tax: –
- Any remuneration or fee received, directly or indirectly, out of the funds made available to an international organization under the technical assistance grant agreement between the international organization and the foreign Government
- Any other income which accrues or arises outside India, and is not deemed to accrue or arise in India in respect of which such consultant is required to pay any income tax (or social tax) to the Government of the country of his or its origin.
However, exemption is available if all the following conditions are satisfied : –
- Such programme is made in accordance with an agreement entered into by the Central Government and a foreign Government ;
- Exemption is available on –
-
- Remuneration received directly or indirectly from the foreign Government on such duties.
- any other income accruing or arising outside India and which is not deemed to accrue to arise in India, provided that such individual is required to pay any income tax/ (or social security tax) to the Foreign Government.
If the individual is not required to pay taxes in the foreign country on such income, he shall be required to pay taxes in India as the exemption would not be available.
MEANING OF CONSULTANT : –
The expression “consultant” has been defined to mean :
a. Any individual who is not a citizen of India or an Indian citizen, who is resident but not ordinarily resident in India; or
b. Any other person being a non-resident engaged by the agency for rendering technical services in India in connection with any technical assistance programme or project in accordance with the agreement entered into by the Central Government and the said agency and such agreement is approved by the Additional Secretary, Department of Economic Affairs in Ministry of Finance, Government of India.
B. REMUNERATION TO EMPLOYEES OF CONSULTANT – SECTION 10(8B) : –
In case of an employee of consultant , following incomes are exempt from tax:
- The remuneration received by an employee of the consultant referred to in Section 10(8A) ;
- Any other income which accrues or arise to such employee of the consultant outside India provided that following conditions are satisfied-
-
- Such income is not deemed to accrue or arise in India
- Such individual is required to pay income tax including, social tax to the Government of the country of his or its origin in respect of such income.
- Such employees is not a citizen of India , or an Indian citizen who is resident but not ordinarily resident in India
- The contract of his service is approved by the prescribed authority before the commencement of his service.
C. INCOME OF FAMILY MEMBER OF SUCH EMPLOYEE
Any family member of such employee (as referred to above in section 10(8), 10(8A) & 10(8B) ), who accompanies the employee to India shall enjoy tax exemption for income which accrues or arises to the family member outside India and is not deemed to accrue or arise in India, provided the family member is required to pay income tax (including social security tax) to the foreign Government or Government of the country of his origin. [Section 10(9)]
INTEREST INCOME ARISING TO CERTAIN PERSON
INTEREST ON NRI BONDS – SECTION 10(15)(iid)
As per Section 10(15) (iid) , interest on certain notified bonds (NRI Bonds and NRI Bonds (Second Series) shall be exempt from tax in the case of following persons : –
- Non-resident Indian (‘NRI’) individual owning such bonds
- Nominee or survivor of NRI at (i) who own such bonds
- An Individual donee, who has been gifted such bonds by such NRI
However, such exemption is available only if following conditions are satisfied : –
- Bonds are purchased by NRI in foreign exchange ;
- Interest and principal received on such bonds is not allowed to be taken out of India (on maturity/ otherwise).
POINTS TO CONSIDER
- “Non-resident Indian” means an individual, being a citizen of India or a person of Indian origin who is not a “resident” (Section 115C). A person shall be deemed to be of Indian origin if he, or either of his parents or any of his grand-parents, were born in undivided India ( Section 115C).
- The exemption shall continue to apply to such NRI who become resident subsequently after purchase of such bonds.
- Exemption shall not apply on interest received by the NRI/ others, in the previous year in which such bonds are encashed prior to their maturity.
- Exemption shall not be available in respect of any further issue of bonds on or after 1.6.2002 (CG shall NOT notify any such bonds post 01.06.2002).
INTEREST PAYABLE TO FOREIGN BANK – SECTION 10(15)(iiia)
Interest payable to any bank incorporated in a country outside India, shall be exempt from tax if : –
i) Such foreign bank is authorised to perform central banking functions in that country; and
ii) Interest is payable on deposit made by such bank with any scheduled bank in India with the approval of the RBI
INTEREST PAYABLE TO NORDIC INVESTMENT BANK – SECTION 10(15)(IIIB)
Interest payable to the Nordic Investment Bank shall be exempt from tax, if the loan is taken for project approved by the Central Government, in terms of the MOU entered into by the Central Government with Nordic Investment Bank on the 25.11.1986.
NOTE :
Nordic investment bank is a multilateral financial institution constituted by the Governments of Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway and Sweden.
INTEREST PAYABLE TO EUROPEAN INVESTMENT BANK – SECTION 10(15)(iiic)
Interest payable/paid to European Investment Bank (EIB), shall be exempt from tax if loan is granted by EIB in pursuance of the framework-agreement for financial co-operation entered into by the Central Government with EIB on 25.11.1993.
INTEREST ON FOREIGN CURRENCY DEPOSITS – SECTION 10(15)(iv)(fa)
Interest payable by a scheduled bank (other than cooperative bank) on deposits in foreign currency shall be exempt from tax if –
i) Deposits are held by a non-resident or a person who is resident but not ordinarily resident in India, and
ii) Acceptance of such deposits by the bank is approved by RBI.
INTEREST ON DEPOSIT IN OFFSHORE BANKING UNIT – SECTION 10(15)(viii)
Interest income on deposit in an offshore Banking unit, shall be exempt from tax if it is received –
- By non-resident or a person who is resident but not ordinarily resident in India;
- Such deposit are made on or after4.2005, and
- Such deposit are made in an Offshore banking unit referred to in section 2(u) of the Special Economic Zones Act, 2005.
NOTE :
As per section 2(u) of the SEZ Act, 2005, Offshore Banking Unit means a branch of a bank located in Special Economic Zone, which has obtained prior approval of RBI.
INCOME OF EUROPEAN ECONOMIC COMMUNITY (EEC) – SECTION 10(23BBB)
Income of European Economic Community (EEC), derived in India by way of interest, dividends or capital gains shall be exempt from tax, if investment is made out of its funds under a scheme notified by the Government.
INCOME OF SAARC FUND FOR REGIONAL PROJECTS – SECTION 10(23BBC) OF INCOME TAX ACT
Any income derived by the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) Fund shall be exempt from tax if it is for Regional Project which was set up by Colombo Declaration.
EXEMPTION RELATING TO CRUDE OIL SALE AND STORAGE
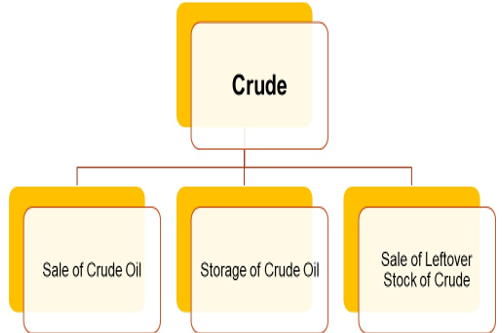
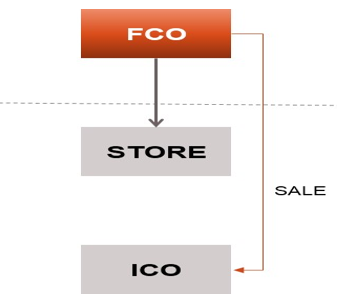
INCOME RECEIVED BY FOREIGN COMPANIES FROM SALE OF CRUDE OIL – SECTION 10(48) OF INCOME TAX ACT
Following incomes received by a foreign company shall be exempt from tax : –
- Income from sale of Crude oil ; and / or
- Income from sale of any other goods or rendering of services as may be notified by the Central Government in this behalf.
However, exemption is available when following conditions are satisfied:
- Income is received in India in Indian currency
- The receipt is pursuant to an agreement with Central Government or approved by Central Government
- The foreign company and the arrangement has been notified by the Central Government in this behalf having regard to the national interest.
- The receipt of the money is the only activity carried out by the foreign company in India.
INCOME RECEIVED BY FOREIGN COMPANIES FROM STORAGE OF CRUDE OIL IN A FACILITY IN INDIA – SECTION 10(48A) OF INCOME TAX ACT
Any income accruing or arising to a foreign company on account of storage of crude oil shall be exempt from tax if following conditions are satisfied : –
- Crude oil is stored in a facility in India.
- Sale of crude oil (from such facility) is made to any person resident in India.
- The storage and sale by the foreign company is pursuant to an agreement with Central Government or approved by Central Government
- The foreign company and the agreement or arrangement is notified by the Central Government, having regard to the national interest .
INCOME ACCRUING OR ARISING TO A FOREIGN COMPANY FROM SALE OF LEFTOVER STOCK OF CRUDE OIL – SECTION 10(48B) OF INCOME TAX ACT
Any income accruing or arising to a foreign company from sale of leftover stock of crude oil, from a facility in India shall be exempt in the following cases : –
- After the expiry of an agreement or an arrangement referred to in section 10(48A), or
- Termination of the said agreement or arrangement referred to in section 10(48A).
NOTES :
- Such exemption would be subject to such conditions, as may be notified by the Central Government in this behalf.
For any queries, please write them in the Comment Section or Talk to our tax expert




